Raster Geoprocessing Toolkit
In GIS, there are two types of basic geoprocessing with raster data analysis: single layer analysis and multiple layer analysis. For the single layer analysis, reclassification or recoding is basically assigning a new range of values to all pixels in the dataset based on their original values. This simplification allows for fewer unique values and cheaper storage requirements. Buffering for raster data tends to approximations representing those cells that are within the specified distance range of the target.
For the multiple layer analysis, the clipping process of raster data results in a single raster that is identical to the input raster but shares the extent of the polygon clip layer. The overlay process of raster data is that the number within the aligned cells of the input grids can undergo any user-specified mathematical transformation. The Boonlean raster overlay methods can use the connector (AND, OR and XOR) to combine the information of two overlying input raster data sets into a single output raster. Similarly, the relational raster overlay method uses relational operators (<, <=, =, <>, >, and =>) to evaluate the conditions of the input raster datasets.
The diagram above shows an example of the connector of Boonlean raster overlay method.
There are 4 types of the scale of study: local operations, neighborhood operations, zonal operations and global operations.


.png)

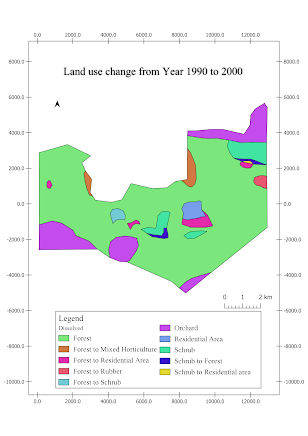
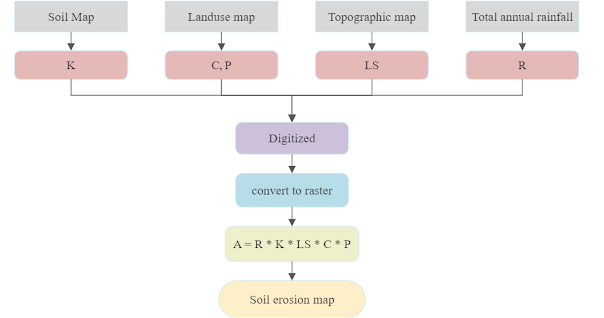
Comments
Post a Comment