Geospatial Data
From the photo above, there are two types of geospatial data: spatial data and attribute data.
Spatial data: any type of data that can be linked to a specific location or geographic area.
Attribute data: includes a wide range of information that describes characteristics of spatial features.
Attribute data: includes a wide range of information that describes characteristics of spatial features.
There are two types of spatial data: vector data and raster data.
- Vector data can be represented by points, lines, and polygons.
Points represent individual locations or features, such as wells, benchmarks, and gravel.
Polygons represent areas, such as the boundaries of a city, a park, water bodies, or a land parcel.
- Raster data are represented as a grid of cells, where each cell is called a pixel and represents a measurement or observation of a specific variable at a particular location on the Earth's surface. It is divided into rows and columns.
- Element of the raster data model :
2) Cell Size - the size of a single pixel which may determine the spatial solution.
3) Raster Bands - each band representing a different variable or aspect of the data.
3) Raster Bands - each band representing a different variable or aspect of the data.
4) Spatial Reference - information that can align with other data.
Rasterization: Vector data --> Raster data
Vectorization: Raster data --> Vector data
Vectorization: Raster data --> Vector data
Comparision between vector data model and raster data model


.png)

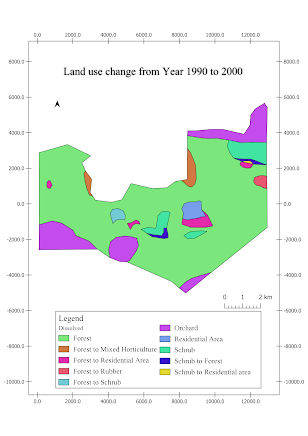
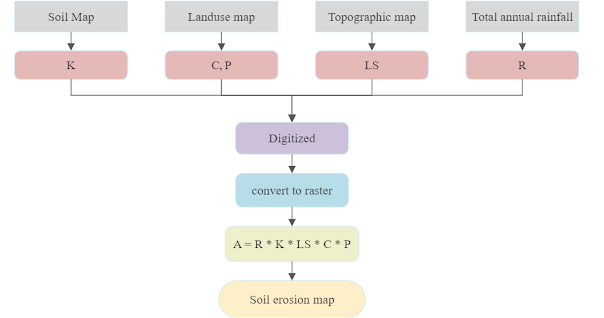
Comments
Post a Comment