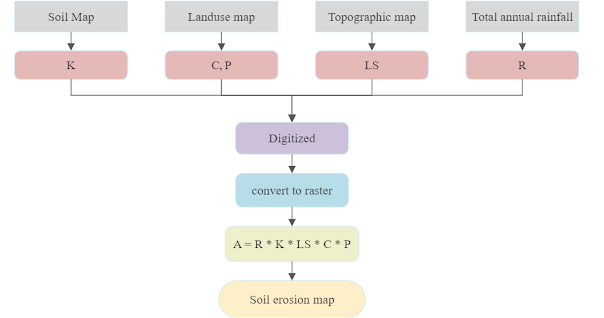
Attribute Data Management
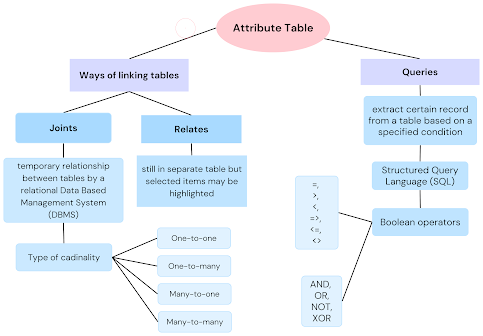.png)
Attribute data refers to non-spatial information that provides details about a spatial feature. Spatial data includes both location information and additional attributes accompanied with it. There are two methods for linking the tables: joining and relating. Joining a table involves establishing a temporary relationship between tables through a relational Data Based Management System (DBMS). The tables need to have a common field and the original stored data remains unaffected. Calculation views can apply a cardinality setting to joins which specifies the number of matching entries in the other tables for each entry in one table. Cardinality types include one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one and many-to-many. On the other hand, relating tables are similar to joins but the tables remain separate and selected items in one table may be highlighted in the table. A query is used to extract specific records from a table based on specified conditions. Many databases utilize ...