Project 2: Land use change analysis
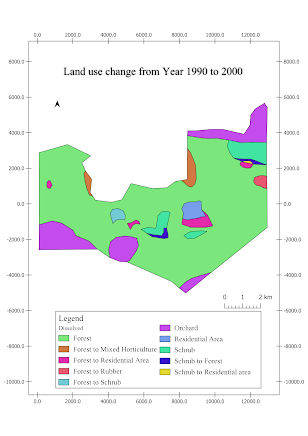
To analysis the land use change by using GIS The land use change map for the Year 1990 to 2000, 2000 to 2010, and 1990 to 2010 are created using QGIS . The graph of land use changes for the Year 1990 to 2000, 2000 to 2010, and 1990 to 2010 are drawn by using Microsoft Excel . Diagram above shows the map of land use change from the year 1990 to 2000. Graph above shows the area change (hectare) of land use change from the year 1990 to 2000. Diagram above shows the map of land use change from the year 2000 to 2010. Graph above shows the area change (hectare) of land use change from the year 2000 to 2010. To get a better visual for soil erosion change for the past 20 years, a map and a graph is drawn. Diagram above shows the map of land use change from the year 1990 to 2010. Graph above shows the area change (hectare) of land use change from the year 1990 to 2010. From the graphs, the area of forest is the largest and the orchard has ...

.png)



